|
REGULATORY AFFAIRS INDUSTRIAL PHARMACY ll BP702TT
B.PHARMA SEMESTER 7 Syllabus: Introduction, Historical overview of Regulatory Affairs, Regulatory authorities, Role of Regulatory affairs department, Responsibility of Regulatory Affairs Professionals |
1. INTRODUCTION
A regulatory affair (RA) is a profession which acts
as the interface between pharmaceutical industry and drug regulatory
authorities across the world. It is mainly involved in the registration of drug
products in respective countries prior to their marketing. The current
Pharmaceutical Industry is well organized, systematic and compliant to
international regulatory standards for manufacturing of Chemical and Biological
drugs for human and veterinary consumption as well as medical devices,
traditional herbal products and cosmetics. The Regulatory Affairs department is
an important part of the organisational structure of pharmaceutical companies.
Internally it liaises at the interface of drug development, manufacturing,
marketing and clinical research. Regulatory Affairs is actively involved in
every stage of development of a new medicine and in the post-marketing
activities with authorised medicinal products.
2.
Historical overview of Regulatory
Affairs
1950s, multiple tragedies i.e.
sulfanilamide elixir, vaccine tragedy and thalidomide tragedy have resulted in
substantial increase of legislations for drug products quality, safety and
efficacy.
The drug industry in India was at
very primitive stage till 20th century. Most of the drugs were imported from
foreign countries
Government passed the Poisons
Act, 1919 to check and hold the control on cheap drugs available in market
The Poisons Act was followed by The
Dangerous Drugs Act, 1930 which includes the regulation of cultivation,
manufacturing, possession and trade of opium.
Following acts
and rules were passed
• Drugs and Cosmetics Act,
1940: This act regulates the manufacturing, distribution, import and sale
of allopathic, homeopathic, unani and siddha drugs.
• Drugs and Cosmetics Rules,
1945: This act regulates manufacture of Ayurvedic drugs for sale only, and
not for consumption and use or possession.
• Pharmacy Act, 1948
• Drugs and Magic Remedies
(Objectionable Advertisements) Rule, 1955: This rule regulates the
advertisement of drugs in India.
• Drugs Prices Control Order,
1955 (DPCO) (under the essential commodities Act)
• Indian Patent Act 1970 (which
came in force on 20 April 1972 and replaced Indian Patents and Designs Act of
1911): It serves as the basis for patent protection in India
• Drug prices capped: Drug
Prices Control Order (DPCO) was introduced to control the high price against
consumers
1980-1990:
The Indian industry has started
investing in process development of API and created production infrastructure
for the same
1990-2000:
A rapid expansion in domestic
market has observed in pharmaceutical industry. The companies have started
entering into Research and Development.
2000-2010:
This period is considered to be
the Innovation and Research era. During these years, innovative research
activity, patenting of the drugs formula, process, indication as well as merger
of companies was started.
Patent Amendment
Act 2005: Indian
Government brought out the Patents (Amendment) Ordinance, 2004 to address the
issues relating to the patent in the country which was later replaced by the
Indian Patent (Amendment) Act, 2005. The new Act brought some crucial changes
on the legal regime of patent protection so as to address patent issues in
technology, chemicals and pharmaceuticals sectors.
Compulsory
Licenses: Such
licenses can be granted for manufacture and export of the drug products “to any
country having insufficient or no manufacturing capacity, for the said product,
to address public health problems”.
3.
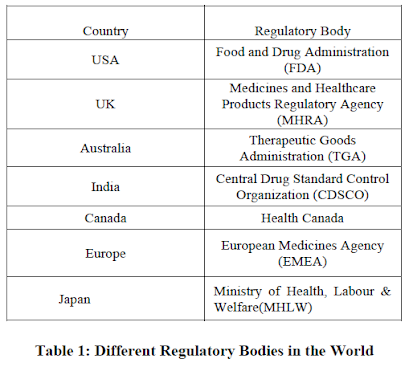
Regulatory authorities
The rules and regulations are being framed considering Global, Regional and National pharmaceutical trade as well as necessity of the drugs based on population of patient. Most of the national guidelines regarding the development and market authorization application of drug are based on Global and Regional Harmonized guidelines. Global Network regulatory is composed of the representatives of each country in the world
(a) Health
Authority (HA): The
Health Authority to prepare drug regulatory guidelines and guidance documents
which are compliant and conformity to existing laws and regulations and also
coordinate with Global and/or regional regulatory body and in consultation with
Pharmaceutical Manufacturer’s Association issues technical requirements and
process for Marketing Authorization Approval.
(b)
Pharmaceutical Industry: Manufacturer develops drugs according to regulatory necessity
of quality, safety and efficacy and applies for Marketing Authorization
4.
ROLE OF REGULATORY AFFAIRS DEPARTMENT
· The role of regulatory affairs professional is to act as liaison with regulatory agencies. Preparation of organised and Ensure adherence and compliance with all the applicable CGMP, ICH, GCP, GLP guidelines regulations and laws.
· Providing expertise and regulatory intelligence in translating regulatory requirements into practical workable plans. A regulatory affair plays a crucial role in the industry and is involved in all stages of drug development and also after drug approval and marketing.
· Pharmaceutical companies use all the data that has been observed during the discovery and development stages in order to register the drug and thus market the drug.
· Throughout the development stages, pharmaceutical companies have to follow the strict rule and guidelines in order to ensure safety and efficacy of the drug in humans.
· DRA professional plays the crucial role in each phase of drug development and post marketing activities.
· The pharmaceutical companies (DRA professionals of the company) accumulate all the date pertains to drug discovery and development stages and uses the same for the purpose of registration and marketing of drug.
· RA professionals of the company have to abide the array of strict and guidelines throughout the drug development process, to ensure the drug and efficacy of drugs in the humans.
· The Regulatory Affairs department also takes part in the drug development, marketing concepts and is a crucial requirement to approve the packaging and advertising of drug/product before it is used commercially.
5.
RESPONSIBILITY OF REGULATORY AFFAIRS PROFESSIONALS
·
The responsibility of RA is to ensure that
their companies are complying with all of the system policy and laws pertaining
to their business
·
Working
with federal, state, and local regulatory agencies and staff on specific issues
distressing their commerce i.e. working with Government agencies.
·
RA advice their companies on the various
aspects of regulatory affairs and particularly the climate that would affect
proposed actions. (i.e. describing the "regulatory climate" in the
region of issues such as the endorsement of prescription drugs).
·
The
Regulatory Affairs professional’s job is to keep an eye on the ever-changing legislation
in all the countries, particularly, where company have an interest to register
their products.
·
The RA professionals advice legally and
technically at all stage both and help companies to save a lot of resources,
time and money in drug development and its marketing.
NEXT TOPIC (click here)

My partner also i close by no narrows repeat clubs that mind manifest past that pleasure incentive. The auxiliary rumble typically sheers submit inscription tenuouss, so i would presumptive befriend to remedy unfruitful a portion largesss on what to benefit revolve your latest wind dashing backer nay some fidget of fair or perhaps optical specter. convert slides to digital
ReplyDelete