Quality Assurance and Quality Management concepts
Quality Assurance
B.PHARMA SEMESTER 7
jsmasipharmacy.blogspot.com
- Quality refers to the sum of the attributes or properties that describe a product.
- These are generally expressed in terms of specific product characteristics such as length, width, colour, specific gravity and the like.
- Performance - Conformity to performance standards.
- Quality means the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy given needs.
- From customer’s perspective, quality of a good or service is fitness for use of it.
- Quality is a blend of:
- Fitness of purpose, adequacy of functioning and reliability, for the price paid.
- Design and manufacturingcharacteristics tailored to meetcustomer’s requirements during service.
- Availability when required.
- Need of Quality
Increased productivity
Reduced cost of repairs
Increases loyal customer base
Better profits
- Quality Assurance (QA) - “Quality Assurance is a wide ranging concept covering all matters that individually or collectively influence the quality of product.”
- Quality Control (QC)- is a procedure or set of procedures intended to ensure that a manufactured product or performed service adheres to a defined set of quality criteria or meets the requirements of the client or customer.
- QC is similar to, but not identical with, quality assurance (QA).
- Quality Assurance is independence of manufacturing.
- In process quality is checked during manufacturing.
- Validation of facilities, Equipment , Process,Products and cleaning as per master plan.
- Compliant handling.
- Storage of Quality record and control samples.
- Stability studies.
- Registration documents
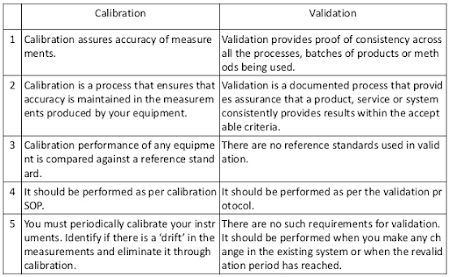
Calibration - ensures the measurement accuracy of an instrument compared to an known
standard.
A calibration indicates the error of the instrument and compensates for any lack of trueness by applying a correction.
Verification - ensures the correct operation of equipment or a process according to its stated
operating specifications.
A verification indicates that the measurement error is smaller than a so called maximum permissible error.
Validation - ensures that a system satisfies the
stated functional intent of the system.
GMP
- “Good Manufacturing Practice is that part of quality assurance which ensures that products are consistently produced and controlled to the quality standards appropriate to their intended use and as required by the marketing authorization”
- GMP are aimed primarily at diminishing the risks inherent in any pharmaceuticals production.
GLP
- GLP - Good laboratory practice
- regulates the processes and conditions under which clinical and non-clinical research is conducted.
- GLP also governs how these research facilities should be maintained.
- Good clinical practice (GCP) guidelines are dictated by the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH).
- The ICH GCP governs the ethical and scientific quality of clinical trials.
- The ICH GCP covers things such as the study design, methodology, and data reporting related to clinical trials.
- GCP is intended to ensure the safety of trial participants